A further explanation
How do astronomers weigh stars & galaxies?
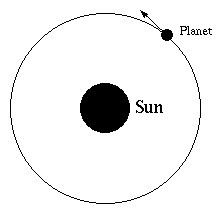
If a planet moves around the sun in a circular orbit of radius r at speed v, then the mass M of the sun is given by:
M= rv2/G
where G is a gravitational constant. If we can measure speed and size of orbit, we can estimate the mass of the central object. For our sun it is about
2,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 kg.
Most solar systems are elliptical rather than circular. The principle's the same, but the arithmetic is harder!
How do astronomers measure distances & sizes?
The Universe is expanding, and so most objects are receding from us. By measuring the redshift we can find out how fast they are moving away.
Cosmological models predict a definite relation between speed and distance; for nearby objects, distance is proportional to speed. This makes it straightforward to decide the distance of say a galaxy.
For objects which are not too far away (and not too small) the difference in angular direction between one boundary and another is directly proportional to its size:
size = angular separation x distance.
Light Years
Particles of light, called photons, move faster than any other object with a speed of three hundred million metres per second. In one year they move a distance 9,500,000,000,000 kilometres, which is called a light year.
If we see light coming from a distant source one million light years away, we are seeing the object not as it is now, but how it was one million years ago.
How do astronomers measure speeds?
Express trains usually sound their horns as they pass through stations at which they do not stop. Passengers on the platform hear a higher note as the train approaches and a lower one as it recedes. The difference in frequency is proportional to the speed of the train. Physicists call this the Doppler effect.
The same effect happens with light. If a star is approaching us it appears bluer, and if it is receding it appears redder. The shift in frequency, usually called the redshift, is proportional to the speed at which it is moving away from us.
