The beginning of the Universe
About fourteen billion years ago, the Universe began in a gigantic explosion - the Hot Big Bang! Its subsequent evolution from one hundredth of a second up to the present day can be reliably described by the Big Bang model. This includes the expansion of the Universe, the origin of light elements and the relic radiation from the initial fireball, as well as a framework for understanding the formation of galaxies and other large-scale structures. In fact, the Big Bang model is now so well-attested that it is known as the standard cosmology.
This tour introduces the Big Bang cosmology and its successes, while emphasising its incompleteness and the areas in which cosmologists are currently working. The key question that interests us, as we delve backwards in time before the standard cosmology, is:
Why was the Universe the way it was at one hundredth of a second?
First, however, you may wish to read about the history of research into the origin of the Universe and the standard cosmology.
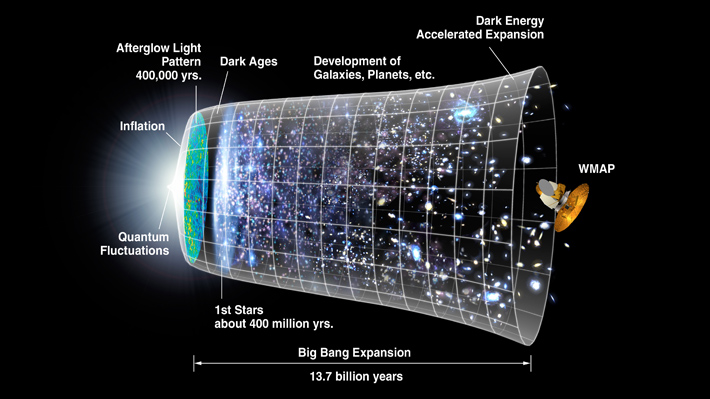
The Universe started approximately 13.7 billion years ago. The latest WMAP and Planck Satellites are able to see remnants of the Universe from when it was just 400,000 years old
